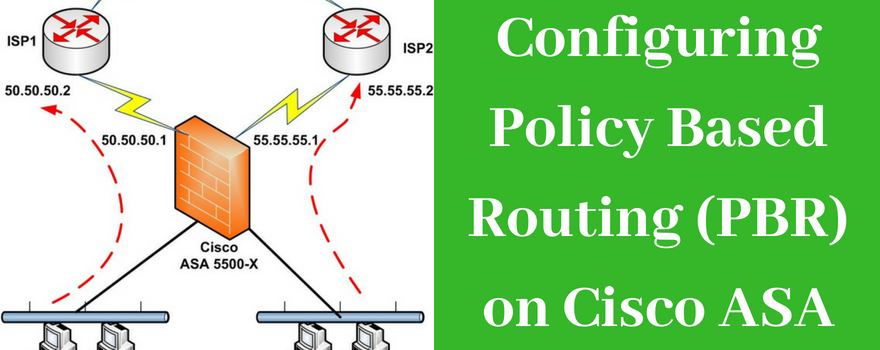
ASA 9.5(2)204 and IOS 15.6 were used in my lab. This is similar to the topology used in Policy Based VPN, however there is a slight difference.The connection between the ASA’s and the ISP routers will use subinterfaces, in order to support routing over different interfaces. View all Alaska Airlines flights and routes here.
With code 9.7 released Cisco decided to add two VERY important features. Route based VPN with VTIs, and bridge groups! This article will show a quick configuration of a route based VPN with ASAs! Previously to do something like this you would need to build a GRE tunnel over IPSEC with a second router terminating GRE.
Notice: Currently OSPF, and EIGRP are not yet supported to run over the tunnel interface. Even with the static neighborship command. The tunnel interface won’t turn to a point-to-point link. So as of 2/19/2017 we must use BGP to advertise over this tunnel. Or we can just use static routes. Also BFD is not supported on the tunnel interfaces yet.

Enters route-map configuration mode. Route map entries are read in order. You can identify the order using the sequencenumber option, or the ASA uses the order in which you add route map entries. Step 2Enter one of the following matchcommands to match routes to a specified destination address. Cisco ASA using multiple Nat/Global commands to nat source IPs to specific public addresses (3 subnets). And then a Cisco router doing PBR to send outbound t. Alaska Airlines, (AS/ASA) - Track Alaska Airlines flights and view detailed fleet information, including number and type of aircraft. See detailed map of the airline’s current routes and read helpful user reviews. Flightradar24 is the world’s most popular flight tracker. IATA: AS ICAO: ASA.
Update: as of 9.9.2 BGP is still the only supported protocol, which is not really an issue as we can always redistribute
I was able to get this to work with 0 packet loss!

Here’s a tease of an up VTI!
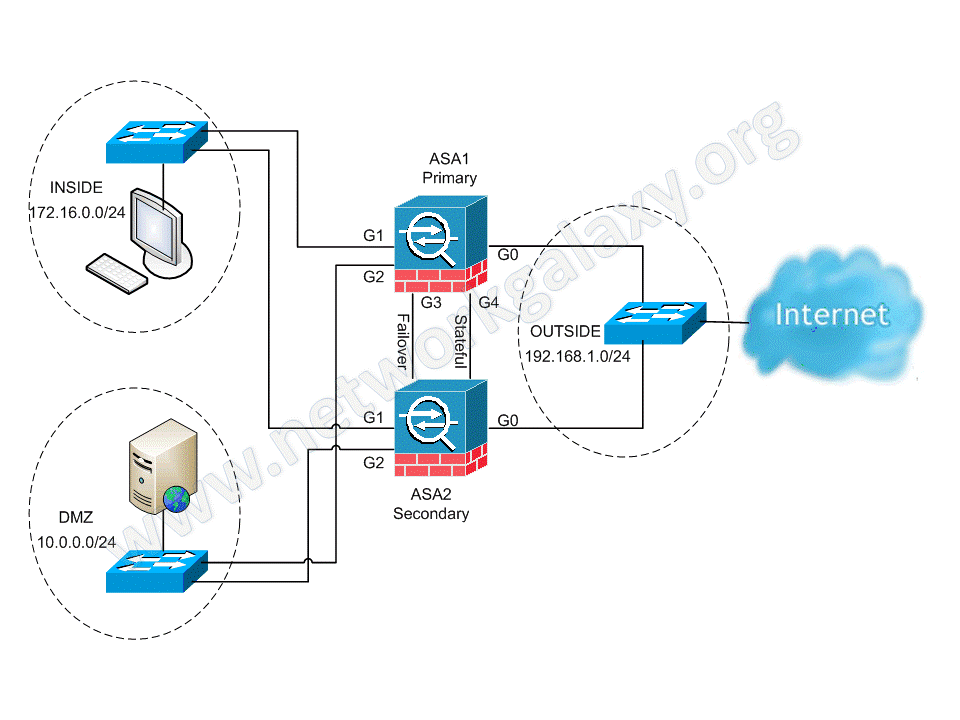
Network Diagram:
First of all let’s apply some good practice config’s to make this tunnel a little more stable and perform better.
Apply the following to both ASA’s:
the first command clamps the TCP MSS/payload to 1350 bytes, and the second command keeps stateful connections even if the vpn temporarily drops.
North ASA config:
South ASA config:
Note: As of code 9.8.1 IKEv2 is now supported as well, if you’re interested in the IKEv2 version for the config, please see below:
assume this is just one side and the wan on the other ASA’s WAN IP is 2.0.0.2 in the below example.
Asa Route Map California
Let’s discuss the config above. There’s a lot going on here. Eachtunnel interface gets its own tunnel-group. They are sharing an ipsec profile. The VTI’s subnets are 10.10.10.0/24 and 10.10.11.0/24. With the VTIs up we now have point to point links we can route over to the other side. Static OSPF or EIGRP neighborships would fit best here. However like I said above they are not supported yet. Thus we need to use BGP. We then configured BGP with private ASNs. We then advertised the LAN subnets to our neighbors and made sure the ASA is their next hop. The BGP feature added was maximum-paths to allow for per session load balancing. We need the static routes for the secondary tunnels because our default route is pointintg towards ISP 1. If we don’t have it then our secondary tunnels will need to renegotiate and failover won’t be so smooth.
Here’s what the routing table looks like now from the North ASA. Notice the BGP route listed twice? That’s because we enabled multipath/maximum paths.
Now let’s test failing over the tunnel interfaces by shutting down the WAN.
Asa Route Map Next Hop
Notice the second tunnel is still up
We get no ping loss to a host on the other wend of the other ASA, 10.0.1.10.
Cisco documentation for reference
